Cervical Cancer – Everything You Need to Know.
Cancer, in general, occurs when cells in a particular body part grow abnormally. Cervical cancer is when the cells in the cervix of a female, begin to grow abnormally. The Cervix is the area that connects the uterus and the vagina.
 Every woman is at risk for cervical cancer. Most of the time, it occurs in women above the age of 30. It has been a medical recurring challenge for the past years. The Bank Hospital is keen on educating the masses. As part of cervical cancer awareness week across the world, here is some basic information you need to know about Cervical Cancer.
Every woman is at risk for cervical cancer. Most of the time, it occurs in women above the age of 30. It has been a medical recurring challenge for the past years. The Bank Hospital is keen on educating the masses. As part of cervical cancer awareness week across the world, here is some basic information you need to know about Cervical Cancer.
Statistics on cervical cancer in Ghana
- Every year about 2797 cases are diagnosed with 1699 deaths
- Second most common after breast cancer
– Source Ghana HPV and related cancers Factsheet 2021
Read more here
Risk Factors.
Although all women are at risk of Cervical Cancer, it is important to take extra care of yourself. The fact that women can get doesn’t mean you should be nonchalant. There are certain risk factors that can increase your chances of getting Cervical Cancer. Here are some of them.
- Women who started having sexual intercourse before 16 years or within a year of starting menses.
- Having multiple sexual partners or a partner with multiple other sexual partners
- Immunodeficiency
- Acute Smokers are at risk of Cervical Cancer
- Sexually transmitted infections especially Chlamydia
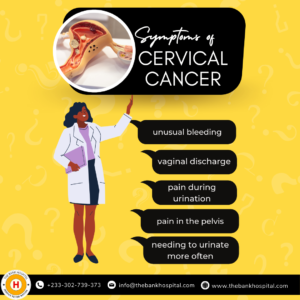
Symptoms.
As a woman, when you see the following symptoms on your reproductive system, be sure to see a physician. These are the common symptoms of cervical cancer.
- Unusual bleeding
- Unusual Vaginal discharge
- Pain during urination
- Pain in the Pelvis
- Unusually Frequent urge to urinate
- Unscheduled menstruation (excessive bleeding)
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Bleeding among women with menopause
It is important to check for unusual symptoms and report them early. If treated early, there is a higher chance of preventing further growth.
Diagnosis
In Pre-cancer or early stages, your physician can help you with diagnosis. Doctors recommend the following
- HPV test and/or Pap test
- Visual inspection with Acetic acid
- Cervical Biopsy for advanced cervical cancer
- CT SCAN/ MRI for advanced stag
Primary Prevention
Cervical Cancer is curable and preventable. The primary prevention of HPV infection include
- Vaccination for boys and girls before they become sexually active
- Partners are encouraged to Reduce the number of sexual partners
- Correct and persistent use of condoms during sexual intercourse
There are currently two vaccines available – Gardasil and Cervarix.
Gardasil 4 is effective against 4 HPV and can prevent anal cancer, throat cancer and genital warts.
Cervarix is effective against only 2 high-risk HPV.
With advancements in medicine, there is currently the new Gardasil 9 which provides effective prevention against 9 HPV infections.
Secondary prevention
This involves early detection of pre-cancer for effective management.
For women 21-29 years, it is recommended to have a Pap test at least every 3 years.
For women 30-65 years, there are three main recommended options.
- Pap test every 3 years
- Both Pap test and HPV screening every 5 years
- Only HPV test every 5 years
Tertiary prevention
Diagnosis and effective treatment to prevent spread and prolong lifespan.
Treatment
There are many options when it comes to the treatment of Cervical Cancer. The most common ones are Surgery, Radiation therapy, Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy.
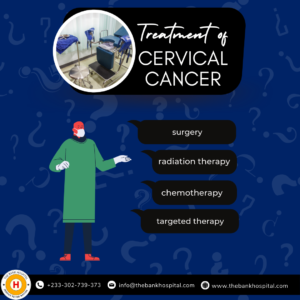
Surgery – The purpose of surgery is to remove as much cancerous growth as possible. Sometimes the physician can remove just the area of the cervix that contains cancerous cells. For more widespread growth, surgery may involve removing the cervix and other affected organs within the pelvis area.
Radiation Therapy – Radiation kills cancer cells using high-energy x-ray beams. It can be delivered through a machine outside the body. It can also be delivered from inside the body using a metal tube placed in the body or vagina.
Chemotherapy – This process uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Doctors give this treatment in cycles. You’ll get chemo for a period of time. You’ll then stop the treatment to give your body time to recover.
Targeted Therapy – This process is similar to chemotherapy in general. This time, the cells are targeted directly section by section using drugs. After the period, the body is given time to recover just like with chemotherapy.
In conclusion, speak to your physician once you see any of these symptoms. As professionals, they will help you with diagnosis and recommend treatment. Our resident Gynaecologis, Dr Emmanuel Adofo is available to help you. You can walk into our front desk anytime or book an appointment via our website.
The Bank Hospital… Service To The Nation.