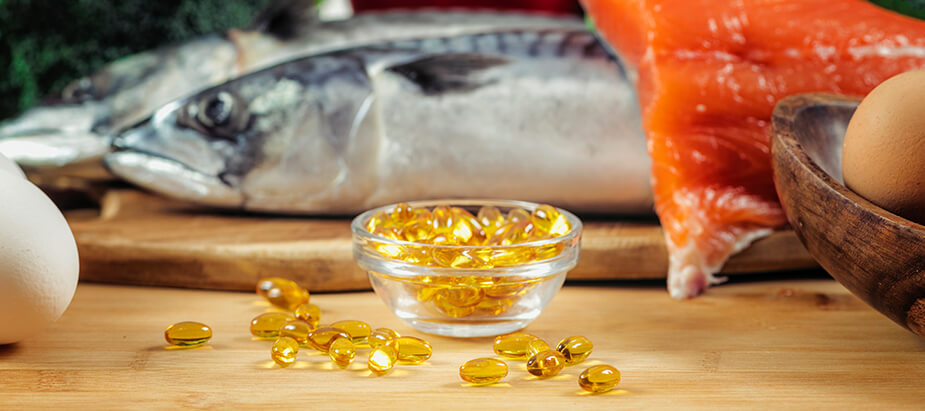
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids that play a crucial role in heart health. They are called essential because our bodies cannot produce them on their own, and we must obtain them through our diet or supplements.
What is Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, while ALA is found in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, hemp seeds, chia seeds, corn oil, and soya bean oils.
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Heart Health
- Reducing Inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, which help reduce inflammation in the body, a major risk factor for heart disease.
- Improving Blood Lipid Profiles: Omega-3 fatty acids help lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and prevent blood clots, all of which contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease.
- Preventing Arrhythmias: Omega-3 fatty acids help regulate heart rhythm and prevent arrhythmias, which can lead to sudden cardiac death.
- Reducing Blood Pressure: Regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids has been shown to lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
Food Sources and Recommended Daily Intake
It is recommended that we consume fatty fish at least twice a week, with a daily intake of 500-1000 mg of EPA and DHA. Plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts can also provide ALA, with a recommended daily intake of 2.4 grams.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in maintaining heart health, and their benefits are backed by extensive scientific research. By incorporating fatty fish and plant-based sources into our diets, including some seeds as snack or added to salads and smoothies, we can reduce our risk of heart disease and promote overall well-being.
By: Ernestina Eduful
Dietician
Dietician